Mix (print): Impose multiple documents at the same time when printing.
Solid: Print a color tint, without gradient and without frame.
Collection: Putting printed sheets in order before stapling them into notebooks, magazines, books.
Flip: Flip a sheet with printing on the front to then print it on the back from the same plate.
Benday: Break down the pantone reference of a four-color process color as closely as possible.
Bitmap: Black and white image at 100% color, with no shades of gray.
Blanket: Rubber form attached to each cylinder of the printing unit. This shape allows the ink to be deposited on the sheet.
Good to roll: At the end of the setting of the machine at the start of printing, the reference sheet which will be used for the duration of the printing.
Good to print (BAT): The printed and signed proof for the customer’s agreement for the launch of the final print.
Bleeds: If you want to print to the edge of the sheet, the graphic composition must be provided 5 mm beyond the cut line. 5mm Bleeds are important to allow for this cut and printed effect (see also “Bleed”).
Stitching : Once assembled, the different signatures are bound together using different techniques (2 stitches, glued square spine, sewn square spine are the main ones).
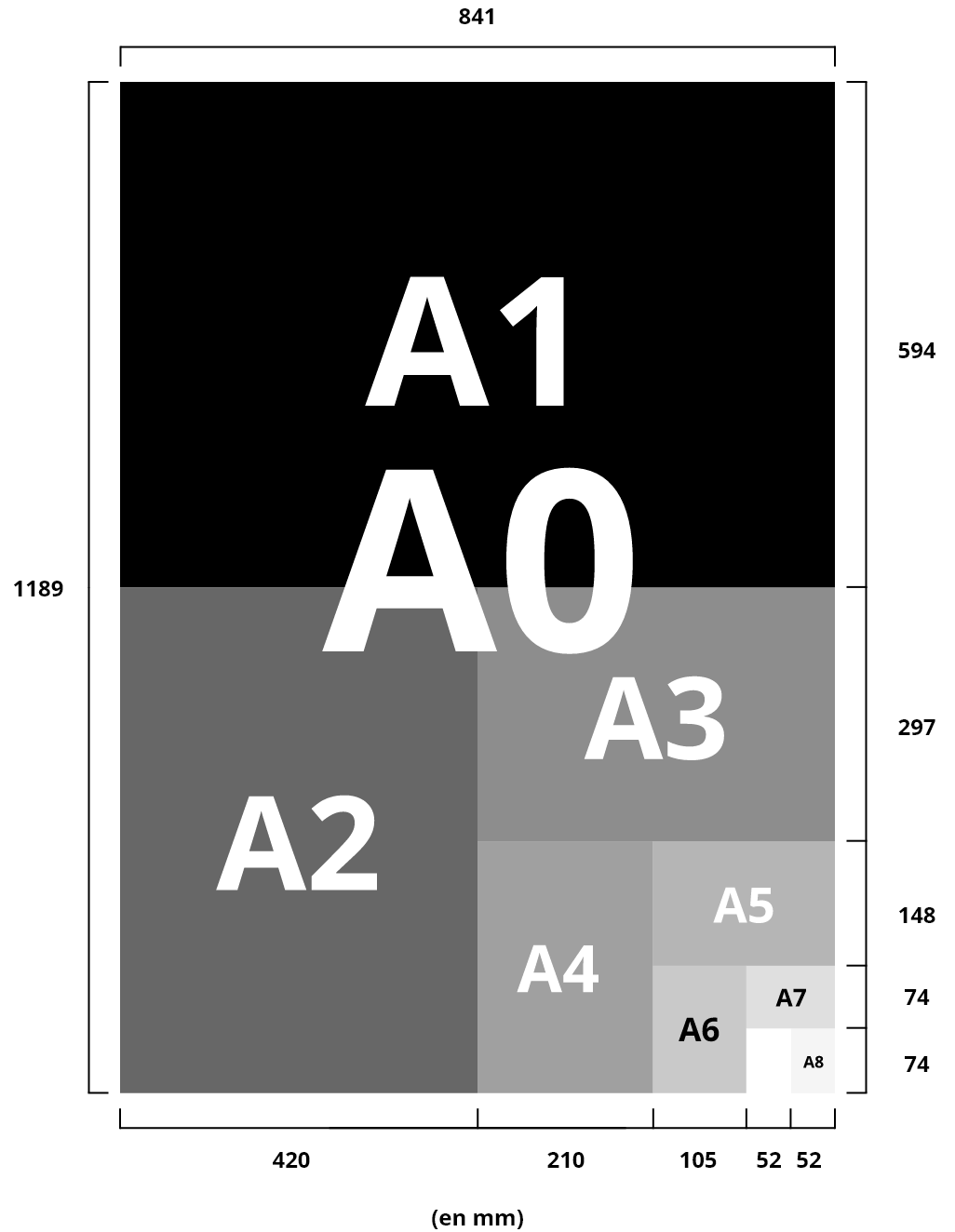
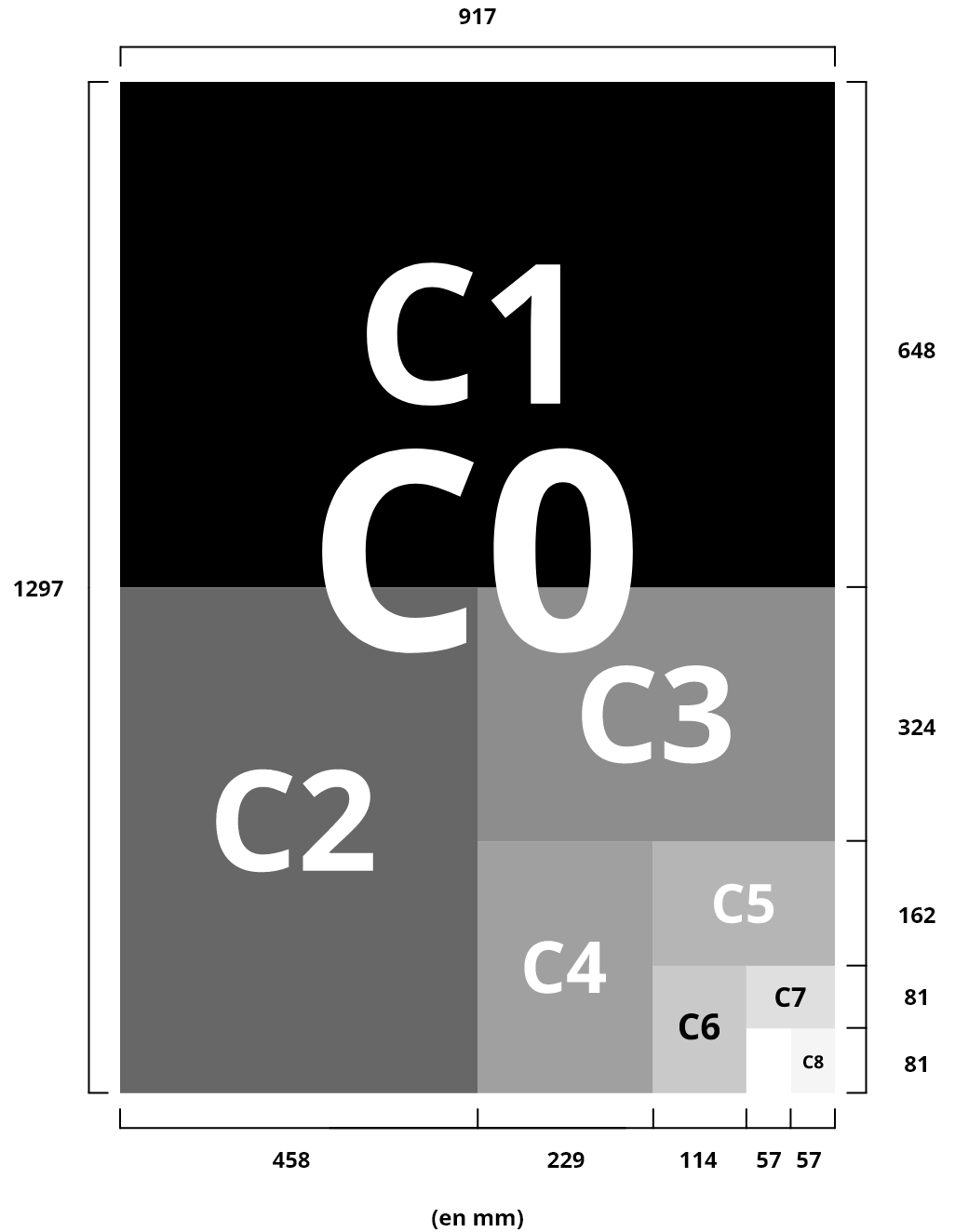
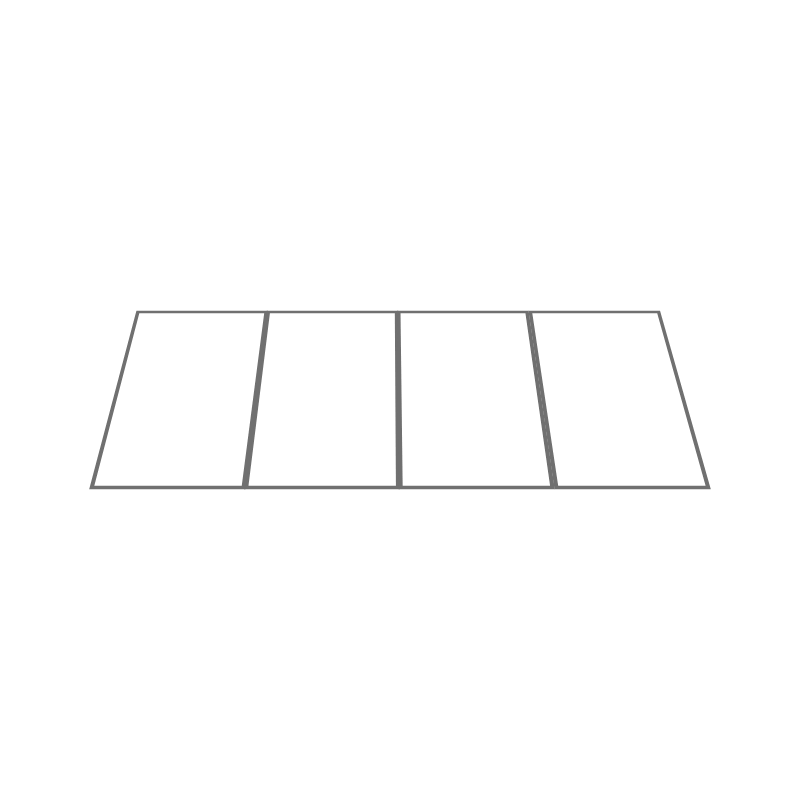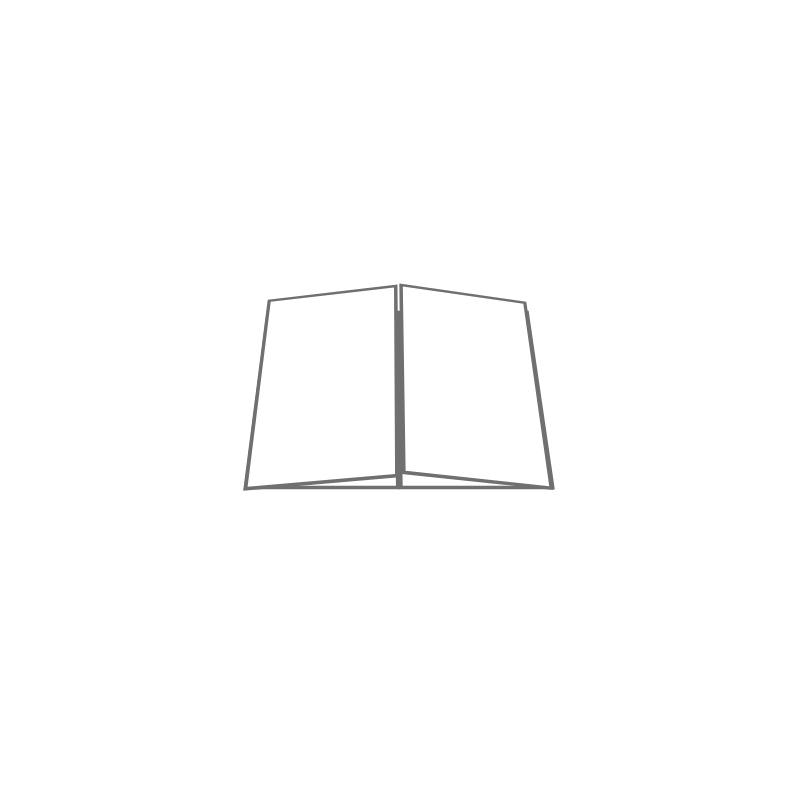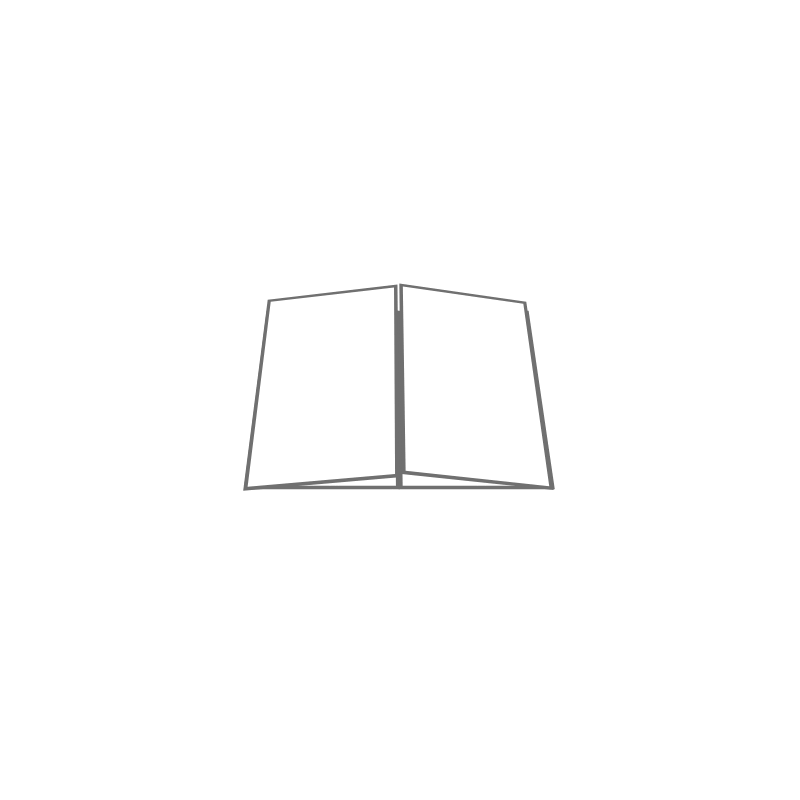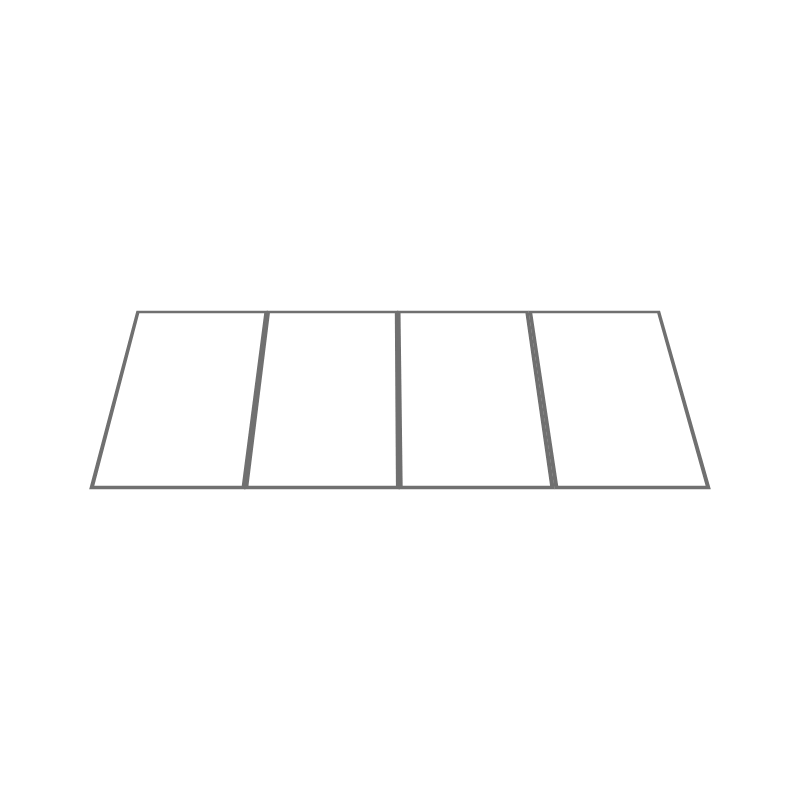
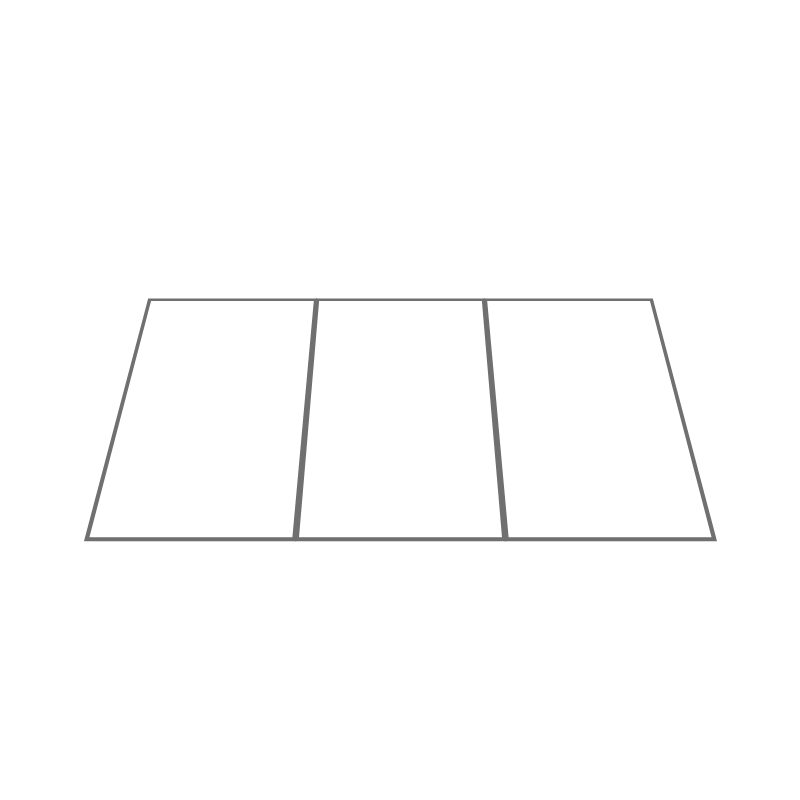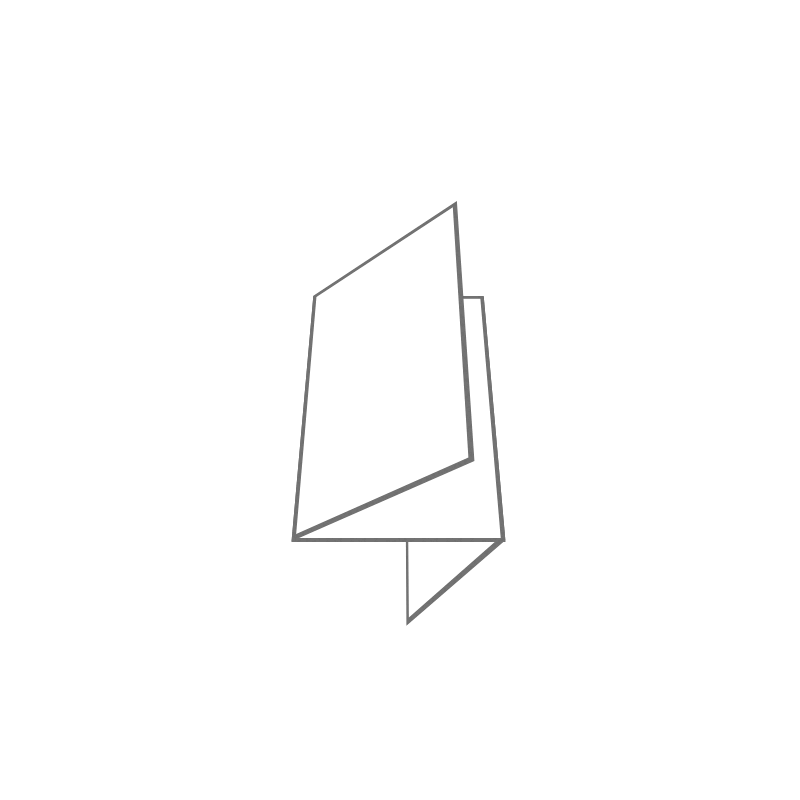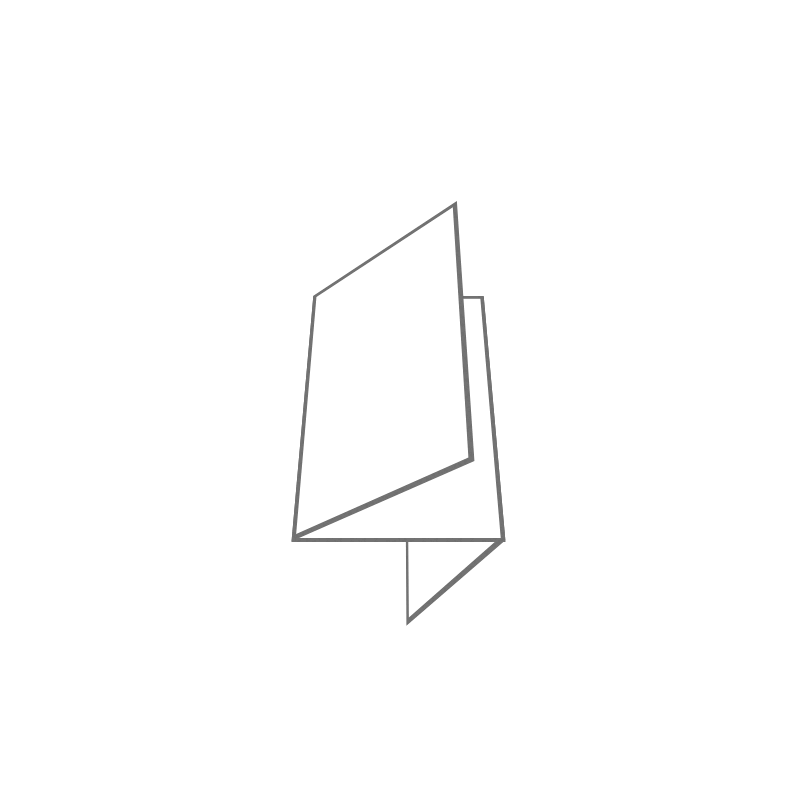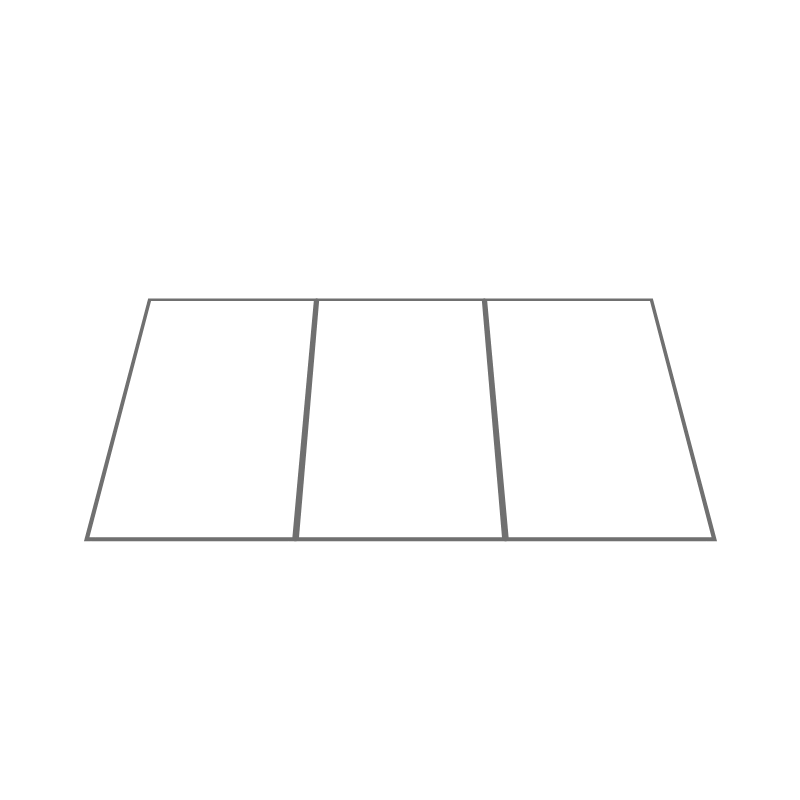
Notebook: Folding a sheet makes it possible to form pages. When 1 fold determines 4 pages, we are talking about a notebook made up of these 4 pages.
Adjustment : Adjust the inking, identify the perfect superposition of colors, but also their density when launching the print in order to obtain the right to roll.
Railway: The layout of a brochure takes into account an assembly plan and the placement of texts and illustrations for a coherent reading result.
CB: Said of a type of glossy coated paper
CM: Said of a type of Matt Coated paper
CMYK: Abbreviation for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black. These 3 primary colors and black (quadrichromy) are used in printing. They are called subtractive primary colors.
Cromalin: It is a document printed from plates and serves as a control and reference to calibrate the colors, before launching a print in the desired quantity.
CTP – Computer to Plate: Technique which consists of passing a document directly from the computer to the printing plates, eliminating the film manufacturing and assembly phases (this technique has become the most common in modern printing).
Knockout: These are text or images left blank in a printed surface (see “Reserve”).
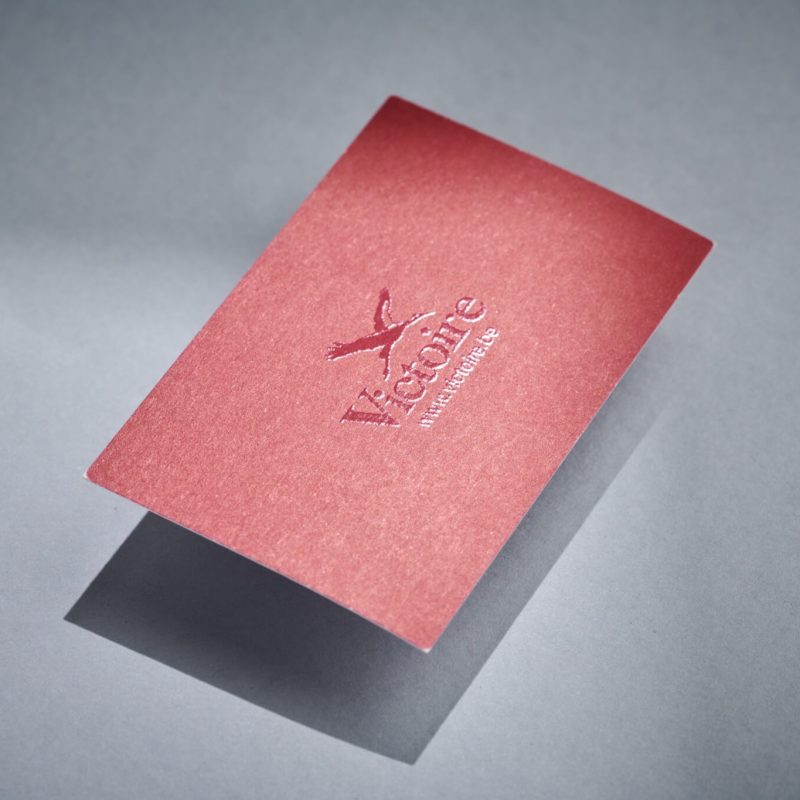
Hot foil: Hot application of gold or silver foil.
Square glued spine: A binding of notebooks glued into the covering cover.
Sewn and glued square spine : A binding bringing together sewn notebooks, then glued into the cover (even more solid process than the previous one).
DPI: Abbreviation in English of “Dot per Inch” which translates to pixels (dots) per inch.
One inch equals 2.54 cm. The higher the number of pixels per inch, the higher the definition of the image. Images in print should be scanned at 300 dpi.
Inserting: Inserting is the act of inserting one notebook into another.
Shaping : Any operation occurring after printing: folding, creasing, cutting, stitching…
Pass Sheets: When initiating a print for color adjustment, sheets are used. It is generally a waste that should be recycled as best as possible.
Bleed: Artwork or solid color that overflows the document (see also “bleeds”).
Landscape format: Format used horizontally. This format is also called Italian format or Oblong.
Portrait format: Format used vertically. This format is also called French format.
Waste: Amount of sheets wasted during the first printing (makeready) and then finishing (cut, fold) stages.
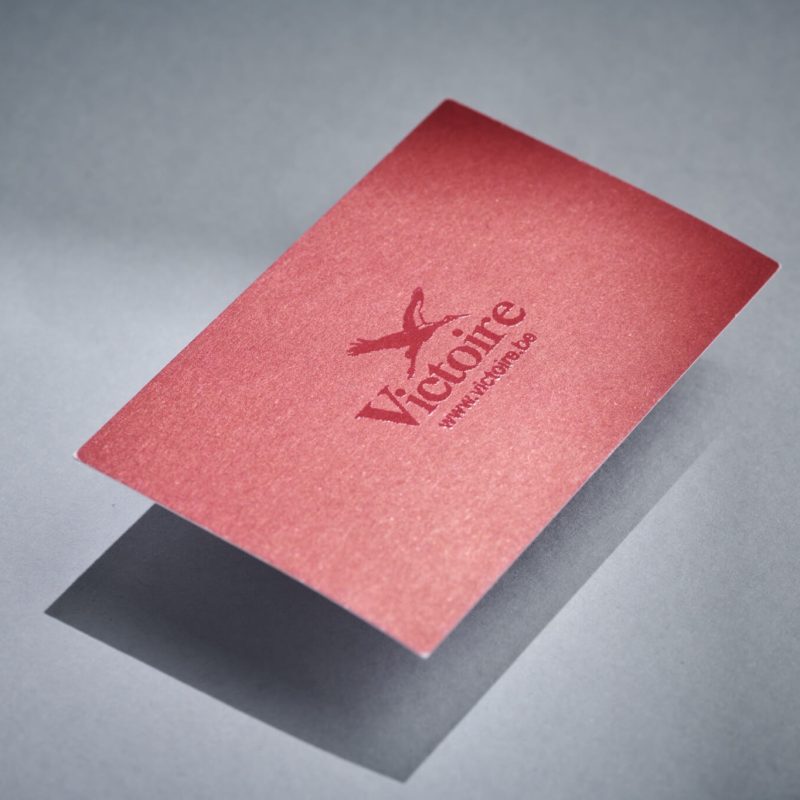
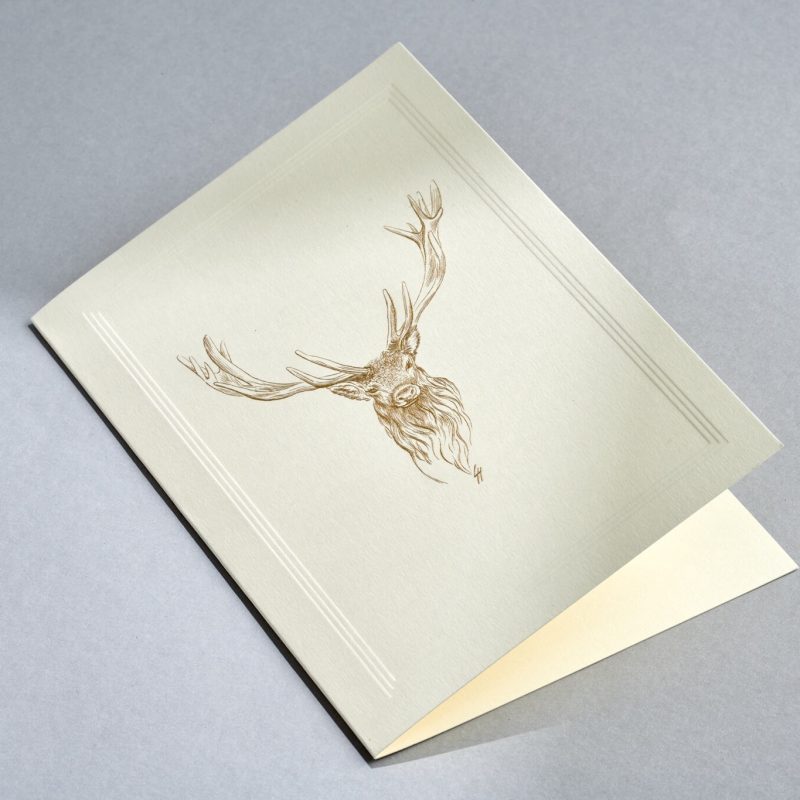
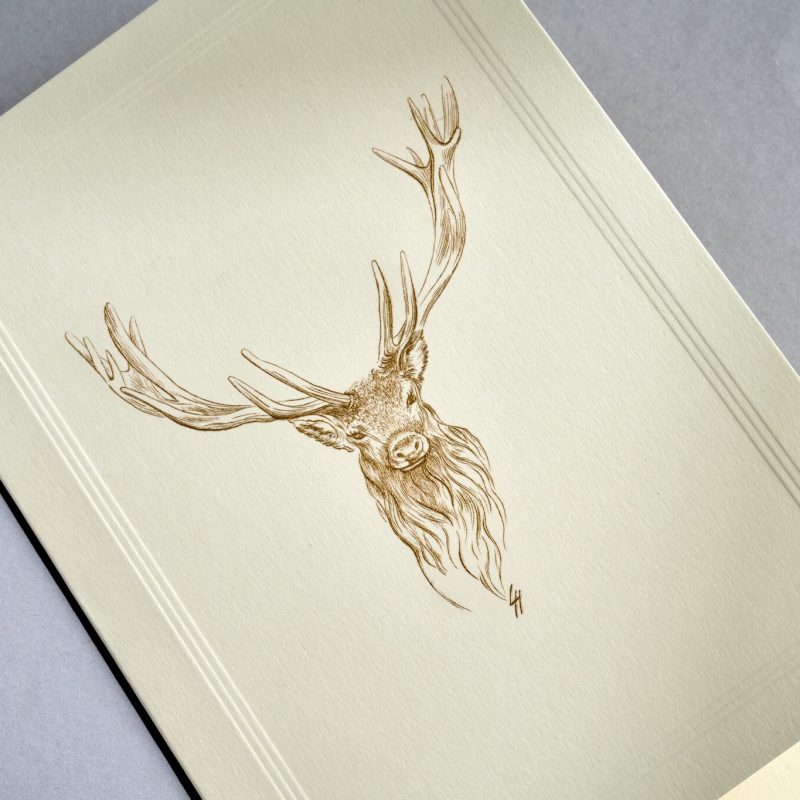
Paper Embossing: Paper Embossing is the act of pinching a sheet into a raised shape (positive, negative, or both) with or without an inked impression.
Grammage: The weight of a sheet per square meter is used as a measure of paper thickness. Choosing a paper therefore means mentioning its weight and